From disease …
Misfolded proteins (α-synuclein, tau, amyloid-β, etc.) are biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s disease.
Similar to prions, they transfer misfolded structures upon contact to previously correctly folded partner proteins.
The results in the formation and elongation of insoluble protein aggregates that accumulate in the brain and disturb normal function.
… to adaptation …
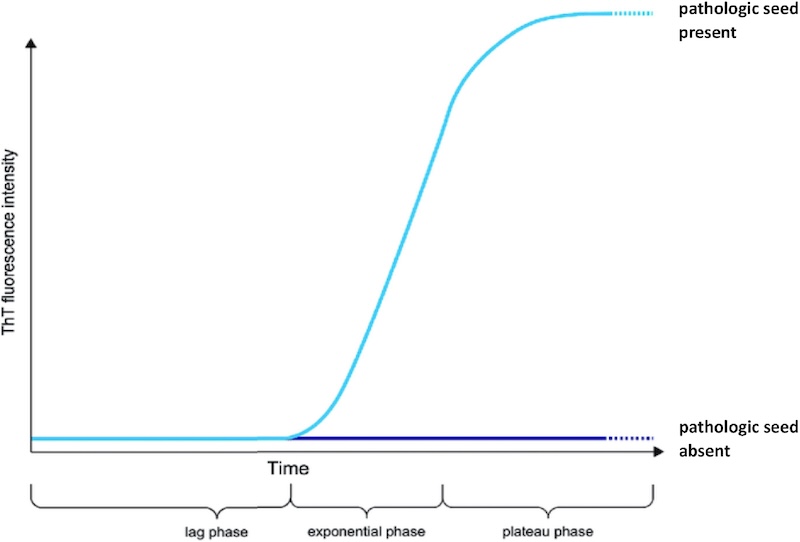
Our IP-background exploits this pathological mechanism for its detection principle.
The misfolded proteins behave as „seeds“ to convert and aggregate correctly folded monomeric
recombinant proteins.
Formed aggregates are then disrupted by shear forces and create new seeds.
The cycle restarts and results in a cyclic amplification: A chain reaction similar to PCR, but with proteins.
 … to drug development
… to drug development
Fluorescence aggregation kinetics of seed-derived protein is utilised for conclusions
about types of disease, disease stages or to create prediction models.
This is our approach to successful and efficient drug development.

SOLUTION
There are currently no analytical devices available that meet the requirements for successful drug development.
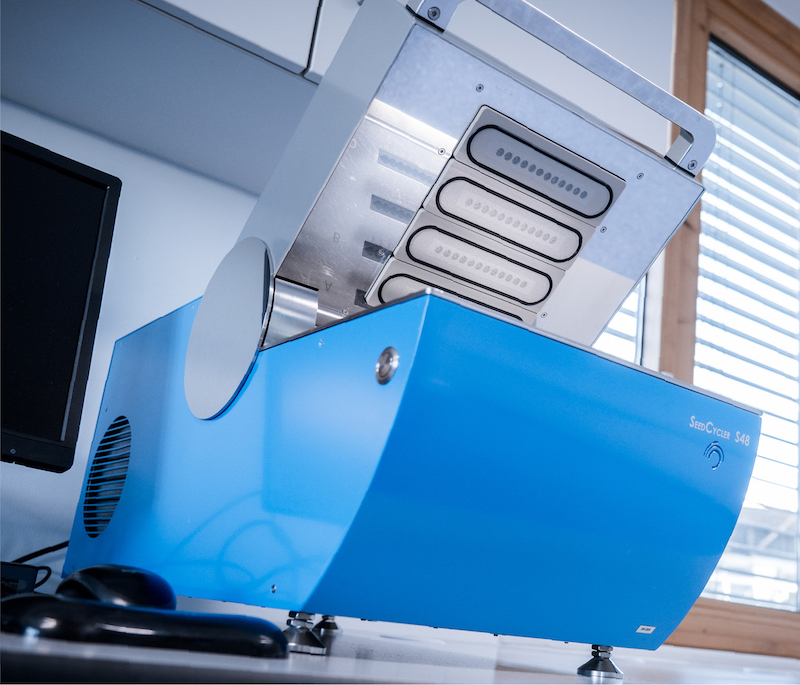
Our SeedCycler is the solution to detect fluorescence aggregation kinetics of seed-derived protein. It is equipped with individually controllable rotation units and lasers for shear force application and measuring the
amplification reaction.
Data analysis, data mining and cluster analysis allow identification of a variety of mutations or strains of (potential) biomarkers.
The technology has been patented and reviewed by independent bodies.